
- #GROUP 7 REACTIVITY TREND MOVIE#
- #GROUP 7 REACTIVITY TREND SERIES#
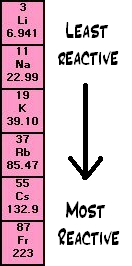
The reason that electronegativity decreases down the group is because each halogen further down the group has an extra inner electron shell shielding the nucleus from the outer electron shell.Īs explained in Periodic Trends: Electronegativity more inner shells make it more difficult to attract electrons into (and keep them held in) the outer shell, which is increasingly further away from the nucleus.This is why fluorine and chlorine are gases at room temperature, bromine is a liquid and iodine a solid. The increasingly large halogen atoms with more electrons produce stronger van der Waals forces between the molecules, so more heat energy is needed to overcome them. F 2, Cl 2, Br 2) get stronger down the group. The reason that melting and boiling points increase down the group is because the intermolecular forces between the halogen molecules (e.g.As with group 1 and 2, the trends in properties and GENERAL reactivity in group 7 can be explained by their electronic configuration:.Iodine is the least reactive halogen (besides astatine which is often ignored because it is extremely rare).
 The halogens get less reactive – fluorine, top of the group, is the most reactive element known. The smallest halogen, fluorine, is the most electronegative element in the periodic table. Electronegativity decreases down the group. The color of the halogens gets darker – fluorine is pale yellow, followed by green chlorine, brown/purple bromine and purple iodine. The melting and boiling point gets higher – starting as gases, bromine is a liquid while iodine is a solid. As you go down the group, the properties of the elements change in the following ways:. They do not conduct heat or electricity. Halogens in elemental form are relatively toxic, reactive substances. They have relatively low melting and boiling points compared to other non-metals (except the noble gases). Halogen ions will usually have a single negative charge (X - ), where they are known as halides. They have a valence of 1 and form covalent bonds with non-metals atoms, or ionic bonds with metal atoms. They are non-metals stable as diatomic molecules (this means at room temperature and pressure, they exist as molecules made of two atoms, e.g. The halogens have the following properties:. As they are reactive elements, they were known and studied in their compounds before being isolated in their reactive, toxic elemental forms. Just like with the alkali metals, the halogens are another example of a well-studied group of elements which display trends in their common properties as you go down the group. The number of outer shell electrons dictates the chemical properties of an element. We have already seen that the Periodic Table is arranged, top-left to bottom-right, by proton number and number of outer shell electrons. To know the key reactions of the halogens. To apply knowledge of electronic structure and bonding to explain the trends in halogens. To understand the trend in properties found in the halogens. This follows the reactivity trend for group 7 Halogens any halogen will displace halide ions from aqueous solution of any members of the group below it in the Periodic Table.
The halogens get less reactive – fluorine, top of the group, is the most reactive element known. The smallest halogen, fluorine, is the most electronegative element in the periodic table. Electronegativity decreases down the group. The color of the halogens gets darker – fluorine is pale yellow, followed by green chlorine, brown/purple bromine and purple iodine. The melting and boiling point gets higher – starting as gases, bromine is a liquid while iodine is a solid. As you go down the group, the properties of the elements change in the following ways:. They do not conduct heat or electricity. Halogens in elemental form are relatively toxic, reactive substances. They have relatively low melting and boiling points compared to other non-metals (except the noble gases). Halogen ions will usually have a single negative charge (X - ), where they are known as halides. They have a valence of 1 and form covalent bonds with non-metals atoms, or ionic bonds with metal atoms. They are non-metals stable as diatomic molecules (this means at room temperature and pressure, they exist as molecules made of two atoms, e.g. The halogens have the following properties:. As they are reactive elements, they were known and studied in their compounds before being isolated in their reactive, toxic elemental forms. Just like with the alkali metals, the halogens are another example of a well-studied group of elements which display trends in their common properties as you go down the group. The number of outer shell electrons dictates the chemical properties of an element. We have already seen that the Periodic Table is arranged, top-left to bottom-right, by proton number and number of outer shell electrons. To know the key reactions of the halogens. To apply knowledge of electronic structure and bonding to explain the trends in halogens. To understand the trend in properties found in the halogens. This follows the reactivity trend for group 7 Halogens any halogen will displace halide ions from aqueous solution of any members of the group below it in the Periodic Table. #GROUP 7 REACTIVITY TREND MOVIE#
Step 4 was repeated with bromine water and chlorine water as shown in the movie clip.Ĭolour changes due to displacement reactions were observed (are clearly visible in the movie clip).Ĭhlorine displaces both bromide and iodide ions from solution.īromine displaces iodide ions from solution.
A few millilitres of aqueous iodine was added to one flask of potassium chloride, one flask of potassium bromide and one flask of potassium iodide and swirled.ĥ. 20ml potassium iodide was put into three 100ml conical flasks.Ĥ. 20ml potassium bromide was put into three 100ml conical flasks.ģ. Approximately 20ml potassium chloride was put into three 100ml conical flasks.Ģ.
#GROUP 7 REACTIVITY TREND SERIES#
A series of free Science Lessons for 7th Grade and 8th Grade, KS3 and Checkpoint Science in preparation for GCSE and IGCSE Science.ġ.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
